A sediment transport study investigates the particular physical processes that govern the motion of sediment in a coastal site and provides an essential tool in coastal management, planning and design.
Sediment transport study contents
A sediment transport study may include several steps, depending on the coastal zone characteristics and the nature of the problem it deals with. It consists mainly of the following:
- Historical shoreline evolution study
- Depth sounding and topographic survey
- Field investigation and photographic documentation
- Sediment sampling and grading tests
- Numerical modeling of coastal sediment transport
Governing mechanisms of a sediment transport study
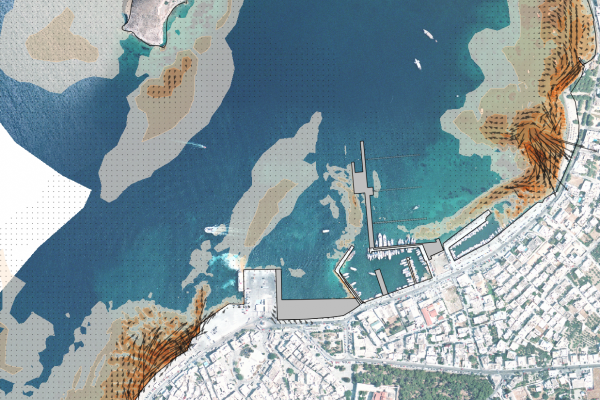
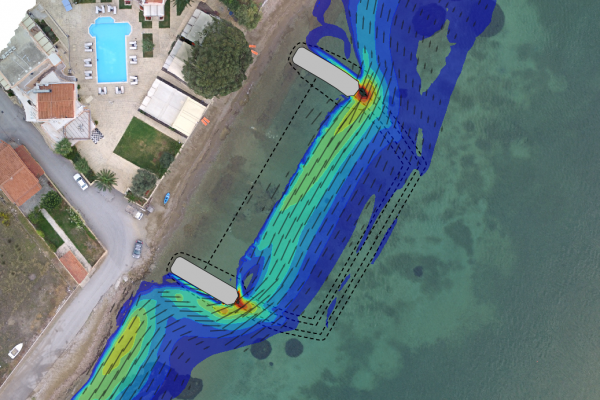
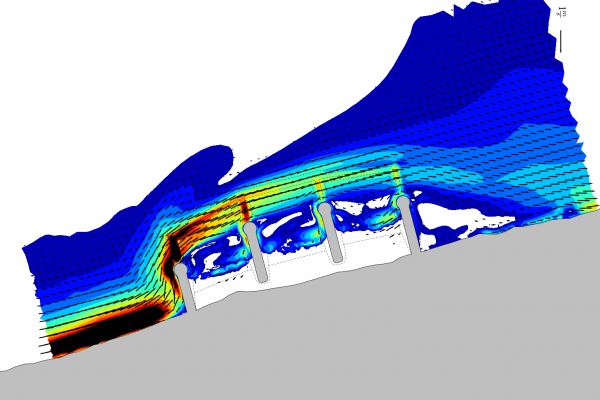
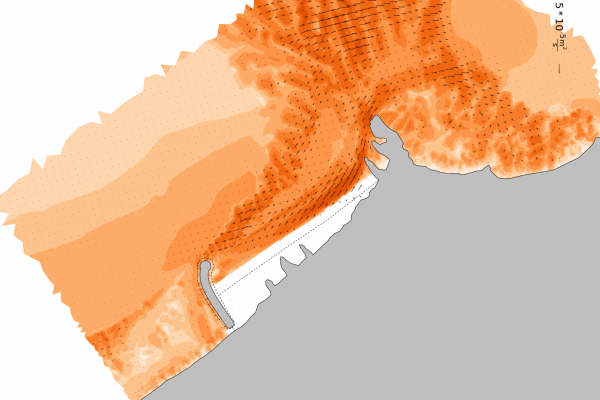
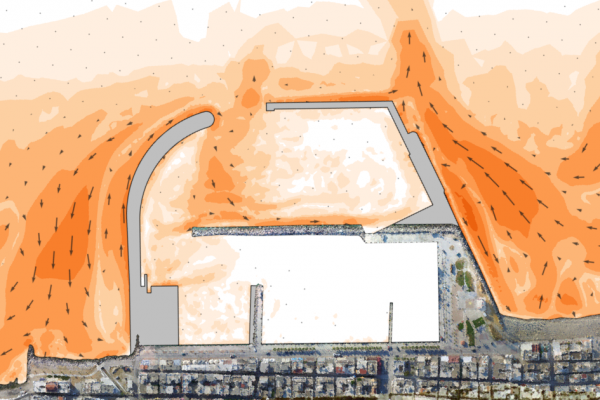
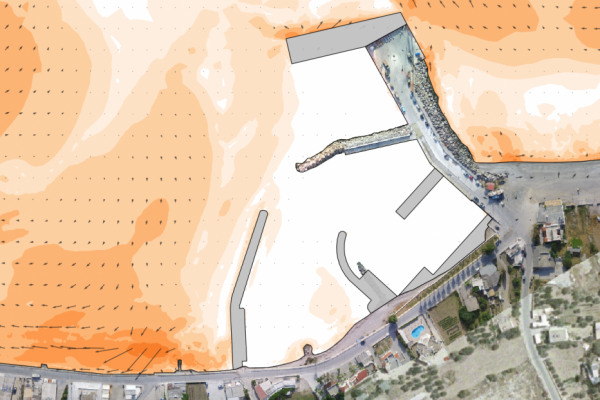
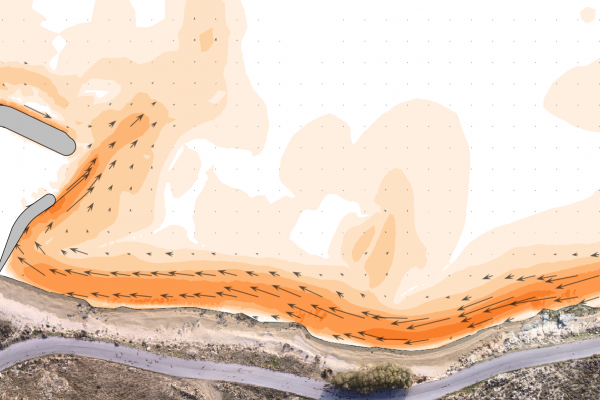
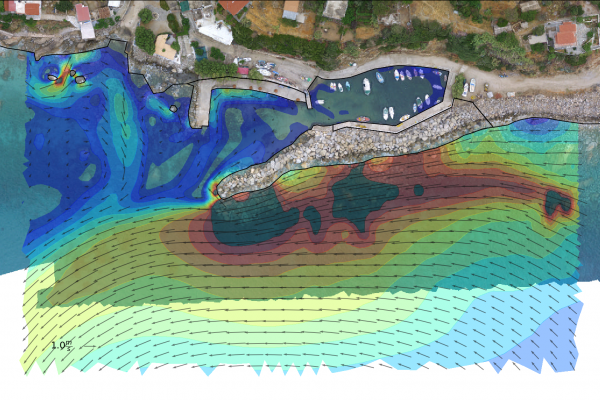
The transformation and breaking of waves over a coastal profile, generates wave setup and currents along the shore that result in mobilization and transport of the sediment (e.g. sand) present in the profile. The primary agents in coastal sediment transport are wind generated waves, followed by tidal currents and storm surge. In addition to the physical processes acting upon the shore, the availability and particle size distribution of the sediment is critical to determine how the profile will respond.
Numerical Modeling
Interpreting the above physical processes is an increasingly complex task that can be dealt with numerical modeling. However, if the results of a simulation are to be reliable, a skillful setting up procedure must be observed. Otherwise the discipline's popular motto "garbage in-garbage out" governs the results.
Our company not only has qualified, experienced personnel, but also is continuously involved in numerical modeling of coastal ecosystems. Consequently, our method has evolved and proven to give reliable results.
The numerical models applied are the internationally recognized suites of Mike21, Telemac-Mascaret System and SeaWorks.
Sediment transport study applications
A sediment transport study is applied in the following cases:
- Coastal erosion control
- Beach nourishment and rehabilitation
- Harbor layout optimisation in the presence of wave action and sediment transport
- Design of coastal defence and protection structures
- Beach morphology study